

3 : a strong sudden desire to do something She resisted the impulse to shout. 2 : the motion produced by a starting force. What is called impulse?ġ : a force that starts a body into motion. Rankine (1865), Alfred George Greenhill (1888) and Robert Edmund Froude (1889). In fluid dynamics, momentum theory or disk actuator theory is a theory describing a mathematical model of an ideal actuator disk, such as a propeller or helicopter rotor, by W.J.M. so Rate of change in moemtum is force and it’s unit is N. Rate of change in moemtum = momentum/time. What is the SI unit of change in momentum? The momentum force of a moving object is calculated by multiplying its mass (weight) by its velocity (speed). Momentum is the force that exists in a moving object. The inertia of rest, inertia of motion, and inertia of direction are the three types of inertia. Linear momentum and angular momentum are the two types of momentum. What is an example of momentum in science? Here are some examples of momentum in everyday life: #1 Momentum of a large truck which is slowed down.

If an object is moving, then an object has momentum. In simple words, it is the quantity that measures the amount of motion present in an object. Momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. A seemingly small object can exert a large amount of force if it has enough momentum. It also describes the force needed to stop objects and to keep them in motion. Momentum is important in Physics because it describes the relationship between speed, mass and direction. Along with values, enter the known units of measure for each and this calculator will convert among units. The calculator can use any two of the values to calculate the third. The Momentum Calculator uses the formula p=mv, or momentum (p) is equal to mass (m) times velocity (v). It is determined by the product of the object’s mass and velocity. Because the object is in motion, it is a vector quantity. Momentum is the quantity of motion that is multiplied by the amount of matter moved and the velocity at which it moves. It can also be related to force by Newton’s second law of motion. Higher the mass of the object, the higher the momentum. Higher the velocity, the higher the momentum. Hint : Momentum is a measure of the velocity of a moving object. In this page you can discover 14 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for momentum, like: motion, force, energy, velocity, angular momentum impulse, impetus, thrust, tide, market share, dynamism and drive. The first of these, momentum, was actually introduced by the French scientist and philosopher Descartes before Newton. Who defined momentum?Īt this point, we introduce some further concepts that will prove useful in describing motion. Momentum is the quantity of motion of a moving body, measured as a product of its mass and velocity. An example of momentum is how quickly a car is moving down a hill. Momentum is defined as the amount of motion occurring in something that is moving, or the force that drives something forward to keep it moving. What is momentum with definition and with example? : a property of a moving body that the body has by virtue of its mass and motion and that is equal to the product of the body’s mass and velocity broadly : a property of a moving body that determines the length of time required to bring it to rest when under the action of a constant force. This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia ( view authors).24 What is the unit velocity? What is the simple definition of momentum? Lectures in Physics - Conservation of Momentum.Physics for Scientists and Engineers (6 ed.). 1: Mechanics, Oscillations and Waves, Thermodynamics (4th ed.). Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Vol. Halliday, David Resnick, Robert (1970).Alternatively, the expression can be seen to reflect that the process is adding adherents, or general acceptance, and thus has more mass at the same velocity hence, it gained momentum. The terminology implies that it requires effort to start such a process, but that it is relatively easy to keep it going. Also momentum is conserved in a electrodynamic system but may change from momentum in the fields to mechanical momentum through the movement of the parts (ie a circular ring around a changing magnetic field may begin to rotate and appear to violate the conservation of momentum).Ī process may be said to gain momentum. In physics, the symbol for momentum is a small p, so the above equation can be rewritten as: The amount of momentum that an object has depends on two variables: the mass and the velocity of the moving object in the frame of reference. If an object is moving in any reference frame, then it has momentum in that frame. 2.1.1.1 Head-on collision (1 dimensional).
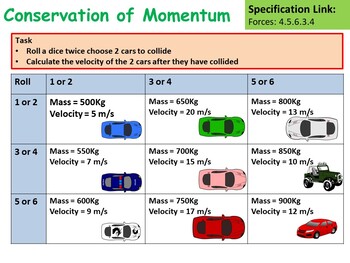
2.1 Conservation of momentum and collisions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
